
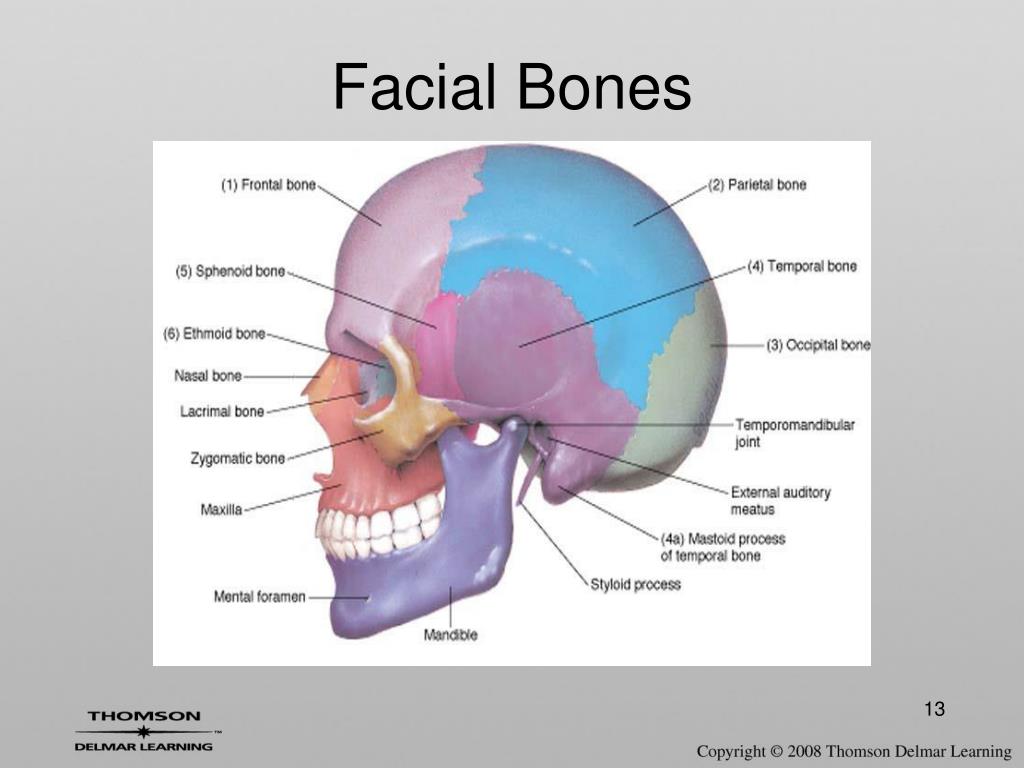
An anterior view of the skull shows the bones that form the forehead, orbits (eye sockets), nasal cavity, nasal septum, and upper and lower jaws. The 22nd bone is the mandible (lower jaw), which is the only moveable bone of the skull.įigure 2. Anterior View of Skull. In the adult, the skull consists of 22 individual bones, 21 of which are immobile and united into a single unit. The rounded brain case surrounds and protects the brain and houses the middle and inner ear structures. The facial bones underlie the facial structures, form the nasal cavity, enclose the eyeballs, and support the teeth of the upper and lower jaws. It is subdivided into the facial bones and the brain case, or cranial vault (Figure 1). The cranium (skull) is the skeletal structure of the head that supports the face and protects the brain. Identify the bony openings of the skull.Identify the bones and structures that form the nasal septum and nasal conchae, and locate the hyoid bone.Name the bones that make up the walls of the orbit and identify the openings associated with the orbit.Define the paranasal sinuses and identify the location of each.

Locate and define the boundaries of the anterior, middle, and posterior cranial fossae, the temporal fossa, and infratemporal fossa.Locate the major suture lines of the skull and name the bones associated with each.List and identify the bones of the brain case and face.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
